Carrier Ethernet is defined by the MEF from the user perspective, as a ubiquitous, standardized, carrier-class service defined by five attributes that distinguish it from familiar LAN-based Ethernet. These attributes are:
- Standardized Services
- Scalability
- Reliability
- Quality of Service
- Service Management
The Standardized Services attribute enables a Carrier Ethernet Service Provider to deliver full range of packet and TDM-based services in an efficient manner.
Carrier Ethernet enables ubiquitous Ethernet services to be provided via standardized equipment independent of the underlying transport media used.
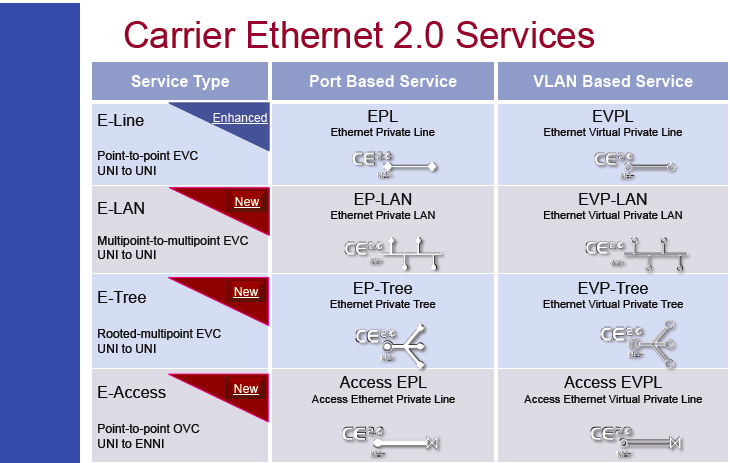
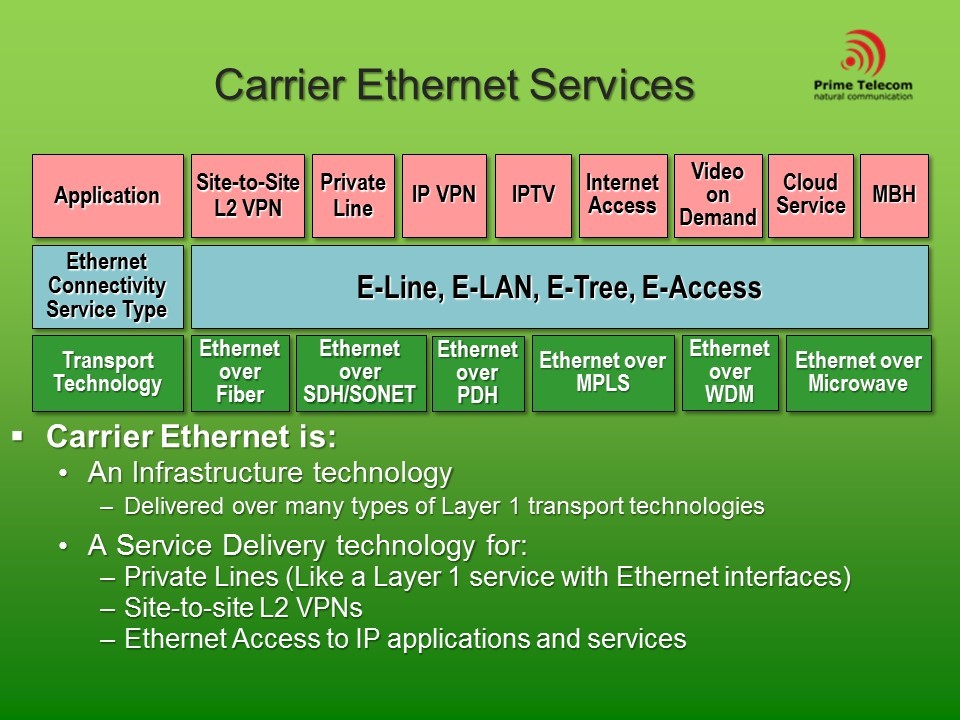
Carrier Ethernet service types :
- E-Line which supports point-to-point Carrier Ethernet services only
- E-LAN which supports multipoint-to-multipoint Carrier Ethernet services
- E-Tree which supports rooted-multipoint Carrier Ethernet services
- E-Access Services
Prime Telecom Carrier Ethernet 2.0 Services Highlights
- CE 2.0 offers a standard, rapid and repeatable method for service providers to add off-net locations to customer services
- Number of new CE 2.0 off-net customer locations to outpace non-CE 2.0 off-net locations 5 to 1 by 2017
- Reduces time and cost to add off-net locations by up to 75%
- Integrated into MEF Certification programs for equipment and services
- All Prime Telecom CE 2.0 services are designed, provisioned and operated by MEF-CECP engineers
Carrier Ethernet 2.0 E-Access Service Steps
- Service Provider and Prime Telecom establish an ENNI
- Service Provider orders an Access EVPL service from Prime Telecom
- Prime Telecom constructs OVCs between OVC End Points at ENNI and out-of-franchise customer UNIs
- Service Provider constructs OVCs between OVC End Points andoff-net customer UNIs
- The concatenation of OVCs forms end-to-end EVCs between on-net and off-net customer UNIs
- Service Provider delivers Carrier Ethernet retail services to customer on-net and off-net UNIs